Configure Conversation Continuity with Email
Conversation continuity

Configuring inbound reply emails
Conversation Continuity requires your chatwoot installation to have a cloud storage configured
There are a couple of email infrastructure service providers to handle the incoming emails that we support at the moment. They are Sendgrid, Mandrill, Mailgun, Exim, Postfix, Qmail and Postmark.
Step 1 : We have to set the inbound email service used as an environment variable.
# Set this to appropriate ingress service for which the options are :
# "relay" for Exim, Postfix, Qmail
# "mailgun" for Mailgun
# "mandrill" for Mandrill
# "postmark" for Postmark
# "sendgrid" for Sendgrid
RAILS_INBOUND_EMAIL_SERVICE=relay
If you wish to use the same local relaying server (for example postfix) to send outbound mail as you are using to relay inbound messages and you opt not to use an external authentication mechanism like SASL which may be the case if the server is handling it own emails only. The upstream SMTP platform Action Mailer attempts to use a default authentication method if the configuration options SMTP_AUTHENTICATION, SMTP_USERNAME and SMTP_PASSWORD are present in your .env file. To disable this behaviour either comment out or delete these lines from your configuration. This will allow you to send outbound messages from the same server without a premium service. Please note many ISP's do not allow email servers to be run from their networks. It is your responsibility to ensure adequate access control preventing yourself becoming an open relay and ensuring your server is able to get past your recipients spam filters for example SPF, DKIM & DMARC dns records.
This configures the ingress service for the app. Now we have to set the password for the ingress service that we use.
# Use one of the following based on the email ingress service
# Set this if you are using Sendgrid, Exim, Postfix, Qmail or Postmark
RAILS_INBOUND_EMAIL_PASSWORD=
# Set this if you are Mailgun
MAILGUN_INGRESS_SIGNING_KEY=
# Set this if you are Mandrill
MANDRILL_INGRESS_API_KEY=
Mailgun
If you are using Mailgun as your email service, in the Mailgun dashboard configure it to forward your inbound emails to https://example.com/rails/action_mailbox/mailgun/inbound_emails/mime if example.com is where you have hosted the application.
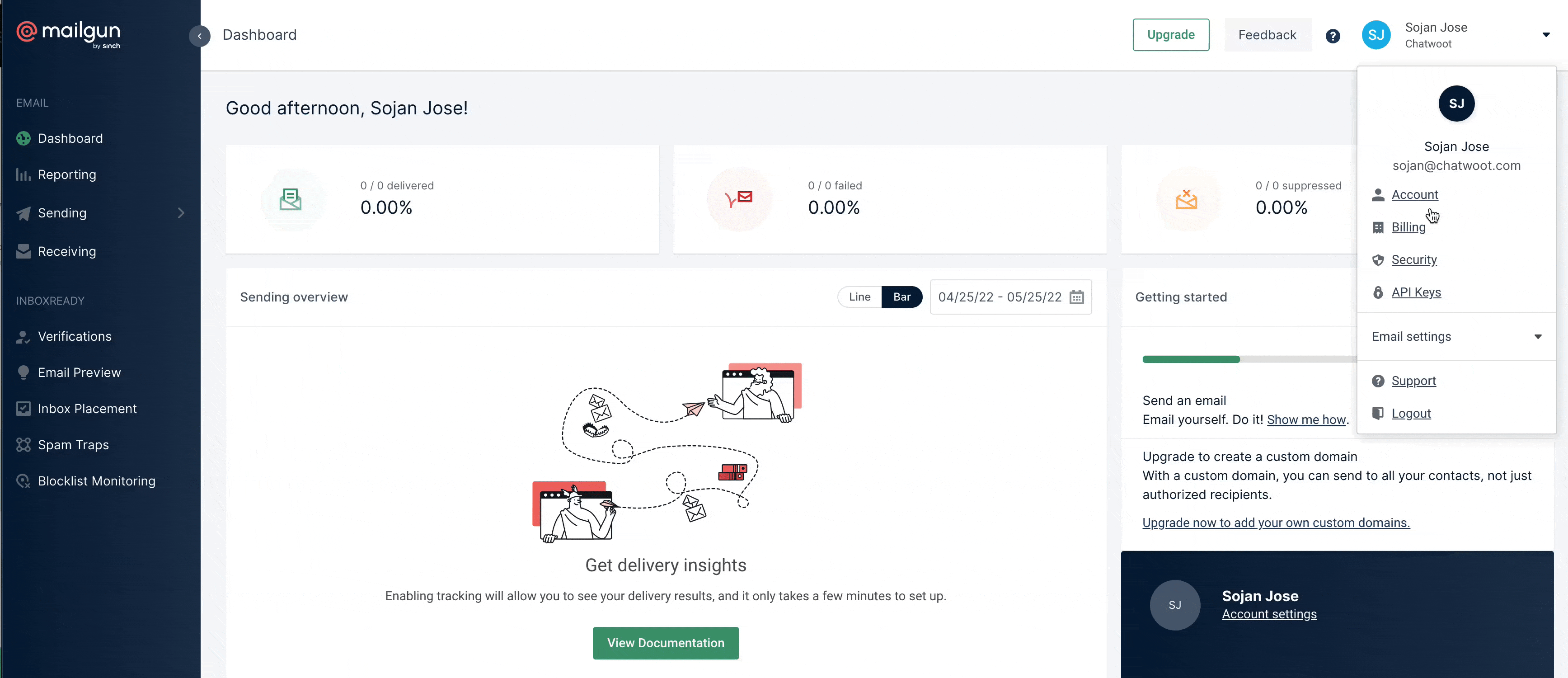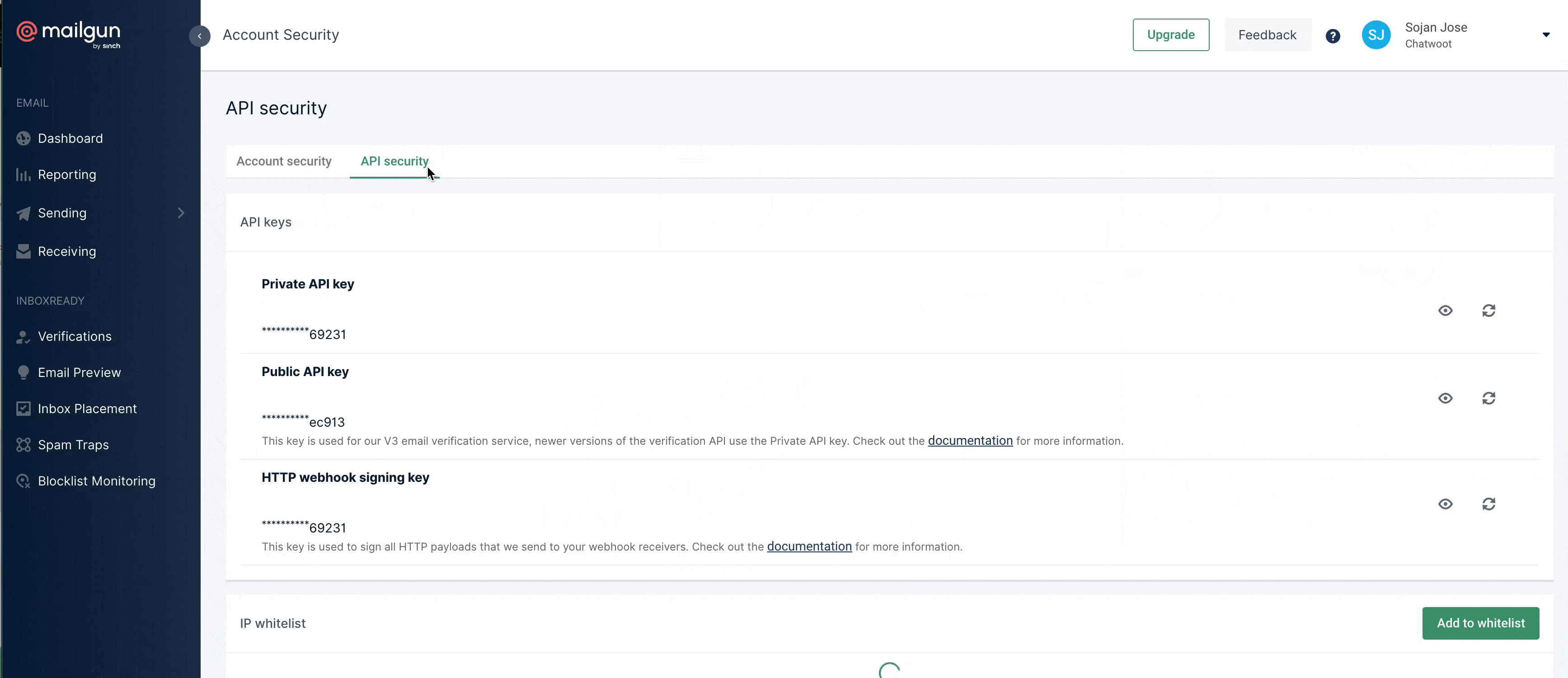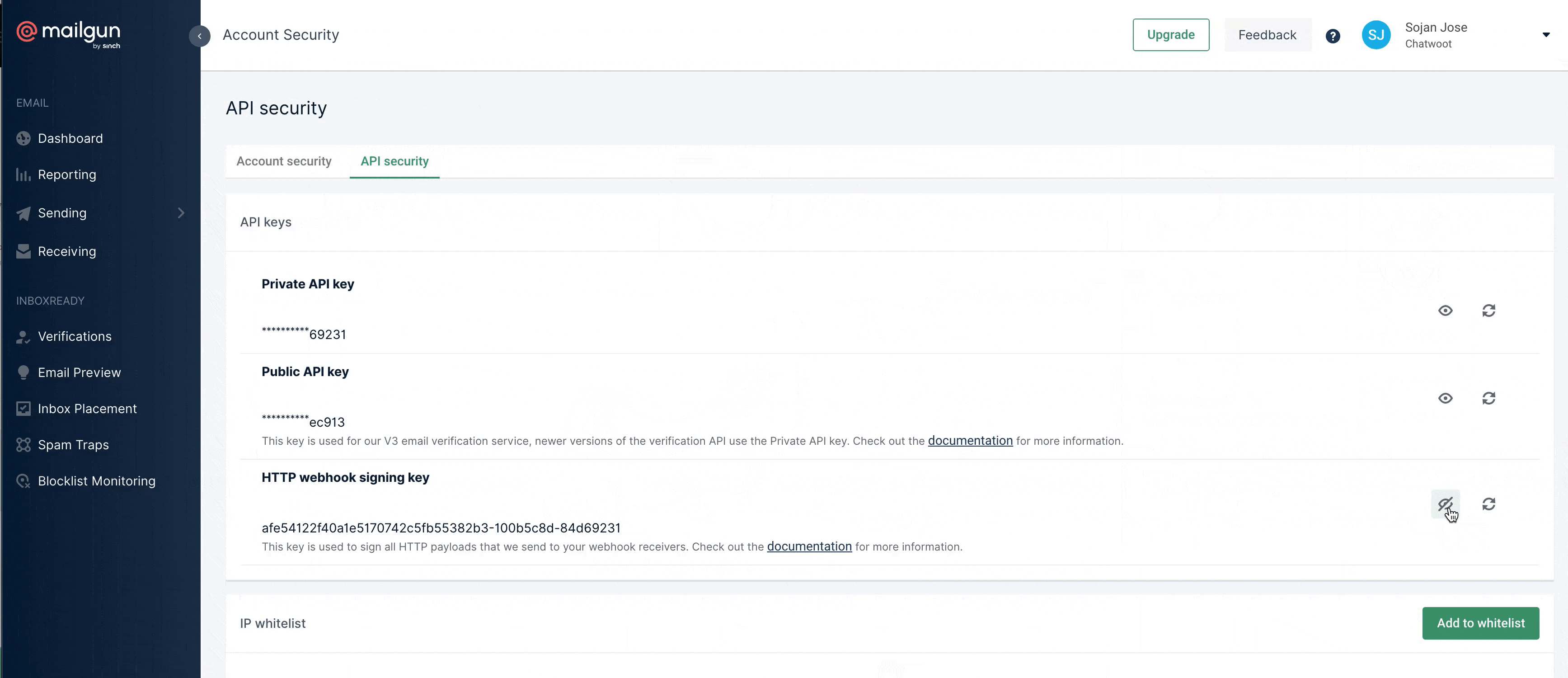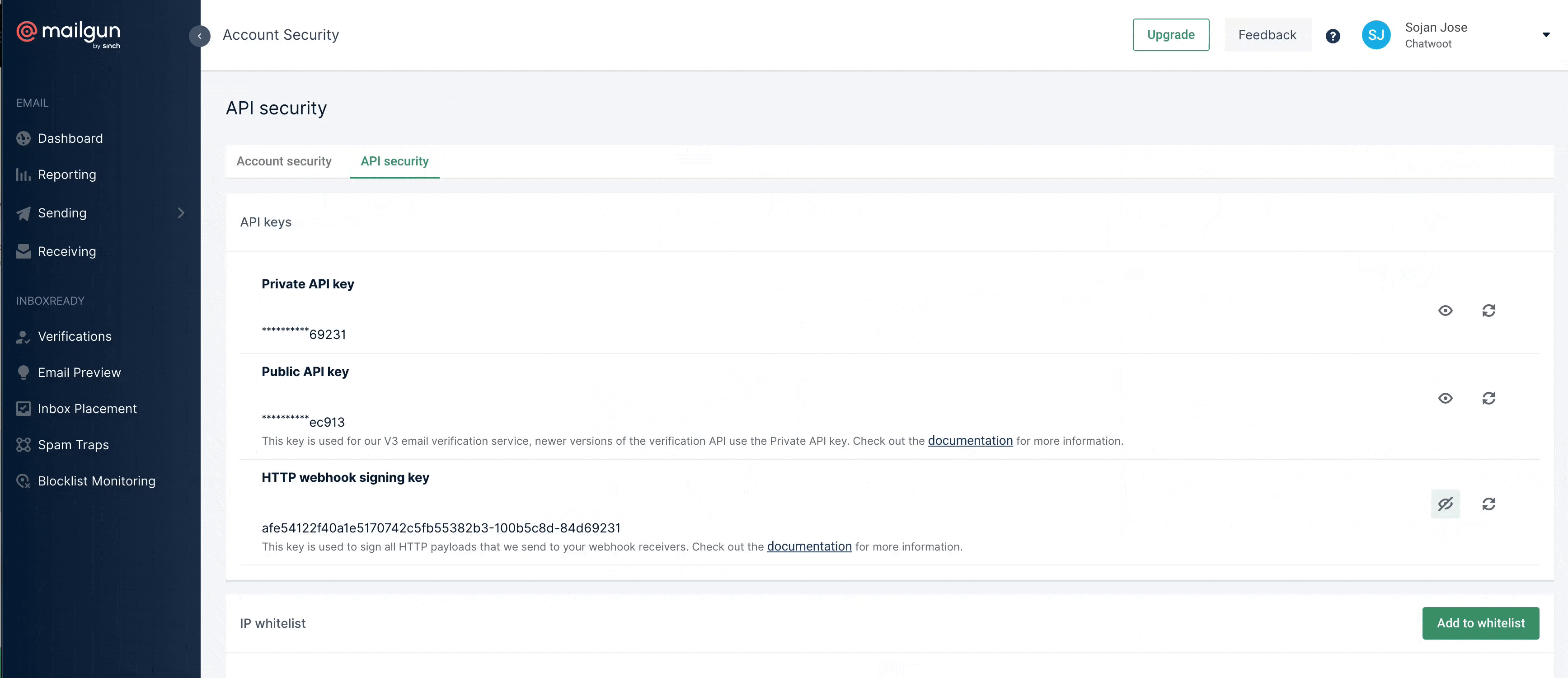
Getting Mailgun Ingress Key
Sendgrid
Ensure to set up the proper MX records for your-domain.com pointed towards Sendgrid
Configure SendGrid Inbound Parse to forward inbound emails to forward your inbound emails to /rails/action_mailbox/sendgrid/inbound_emails with the username actionmailbox and the password you previously generated. If the deployed application was hosted at example.com, you can configure the following URL as the forward route.
https://actionmailbox:PASSWORD@example.com/rails/action_mailbox/sendgrid/inbound_emails
When configuring your SendGrid Inbound Parse webhook, be sure to check the box labeled “Post the raw, full MIME message.” Action Mailbox needs the raw MIME message to work.
Mandrill
If you are configuring Mandrill as your email service, configure Mandrill to route your inbound emails to https://example.com/rails/action_mailbox/mandrill/inbound_emails if example.com is where you have hosted the application.
If you want to know more about configuring other services visit Action Mailbox Basics
IMAP via getmail
UniLink receives inbound emails through the Action Mailbox feature of Ruby on Rails. Action Mailbox supports various 'ingresses' by default. They are defined in here and can be executed through bin/rails. For example
cat my_incoming_message | ./bin/rails action_mailbox:ingress:postfix \
RAILS_ENV=production \
URL=http://localhost:3000/rails/action_mailbox/postfix/inbound_emails \
INGRESS_PASSWORD=...
would import the contents of the file my_incoming_message into a UniLink instance running on localhost - assuming my_incoming_message contains an RFC 822 compliant message.
The ingress tasks provided by Action Mailbox are a thin layer around an HTTP endpoint exposed by Action Mailbox. An alternative to using those tasks is to talk to the http endpoint directly. The following script achieves the same.
INGRESS_PASSWORD=...
URL=http://localhost:3000/rails/action_mailbox/relay/inbound_emails
curl -sS -u "actionmailbox:$INGRESS_PASSWORD" \
-A "Action Mailbox curl relayer" \
-H "Content-Type: message/rfc822" \
--data-binary @- \
$URL
The popular mail retrieval system getmail6 can be used to fetch mails and import them into UniLink. If the curl script above is stored in /home/chatwoot/bin/import_mail_to_chatwoot, a configuration for doing so from an IMAP inbox is as follows.
[retriever]
type = SimpleIMAPSSLRetriever
server = ...
username = ...
password = ...
[destination]
type = MDA_external
path = /home/chatwoot/bin/import_mail_to_chatwoot
[options]
verbose = 0
read_all = false
delete = false
delivered_to = false
received = false
message_log = /home/chatwoot/logs/import_imap.log
message_log_syslog = false
message_log_verbose = true
For mail to be imported you'll need to execute getmail regularly, for example using a cron job. For IMAP you can also run it constantly using getmail --idle INBOX, though that will need some care to deal with interrupted connections, etc.
Configure inbound email domain environment variable
Add the following environment variable with the value your-domain.com, where your-domain.com is the domain for which you set up MX records in the previous step.
MAILER_INBOUND_EMAIL_DOMAIN=
After finishing the set up, the mail sent from UniLink will have a replyto: in the following format reply+<random-hex>@<your-domain.com> and reply to those would get appended to your conversation.